 Treaty of Versailles, 1919
Treaty of Versailles, 1919
 Nazi-Soviet Pact, 1939
Nazi-Soviet Pact, 1939
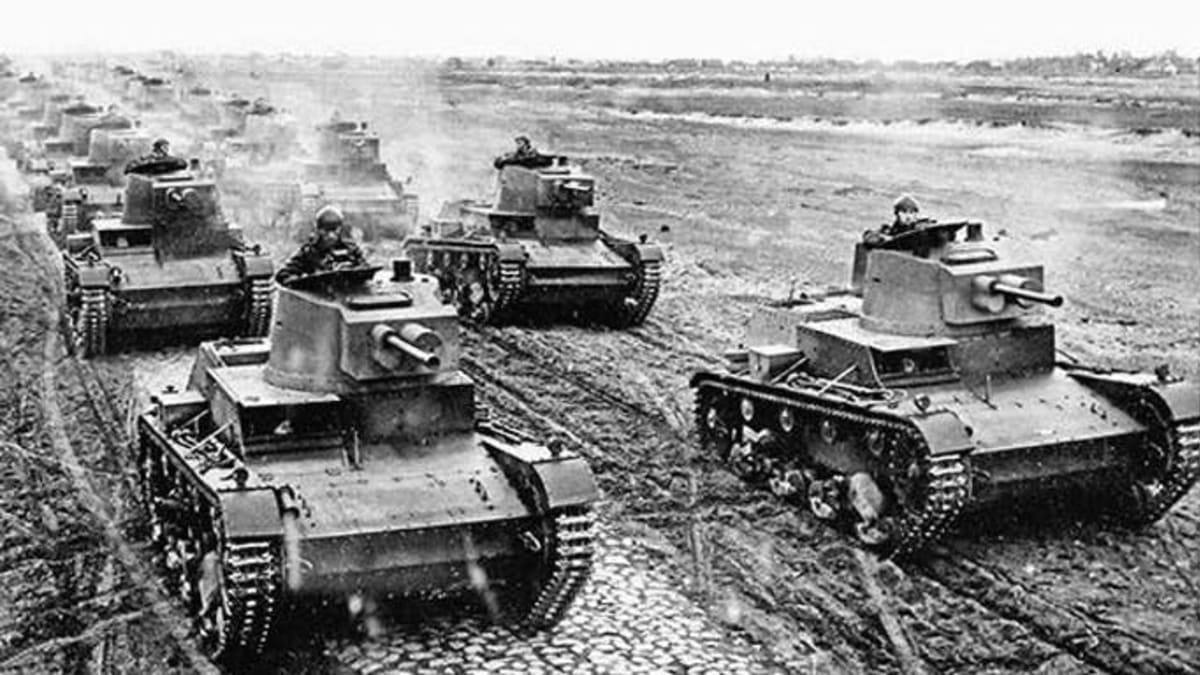 German tanks used in blitzkrieg, 1939-1942
German tanks used in blitzkrieg, 1939-1942
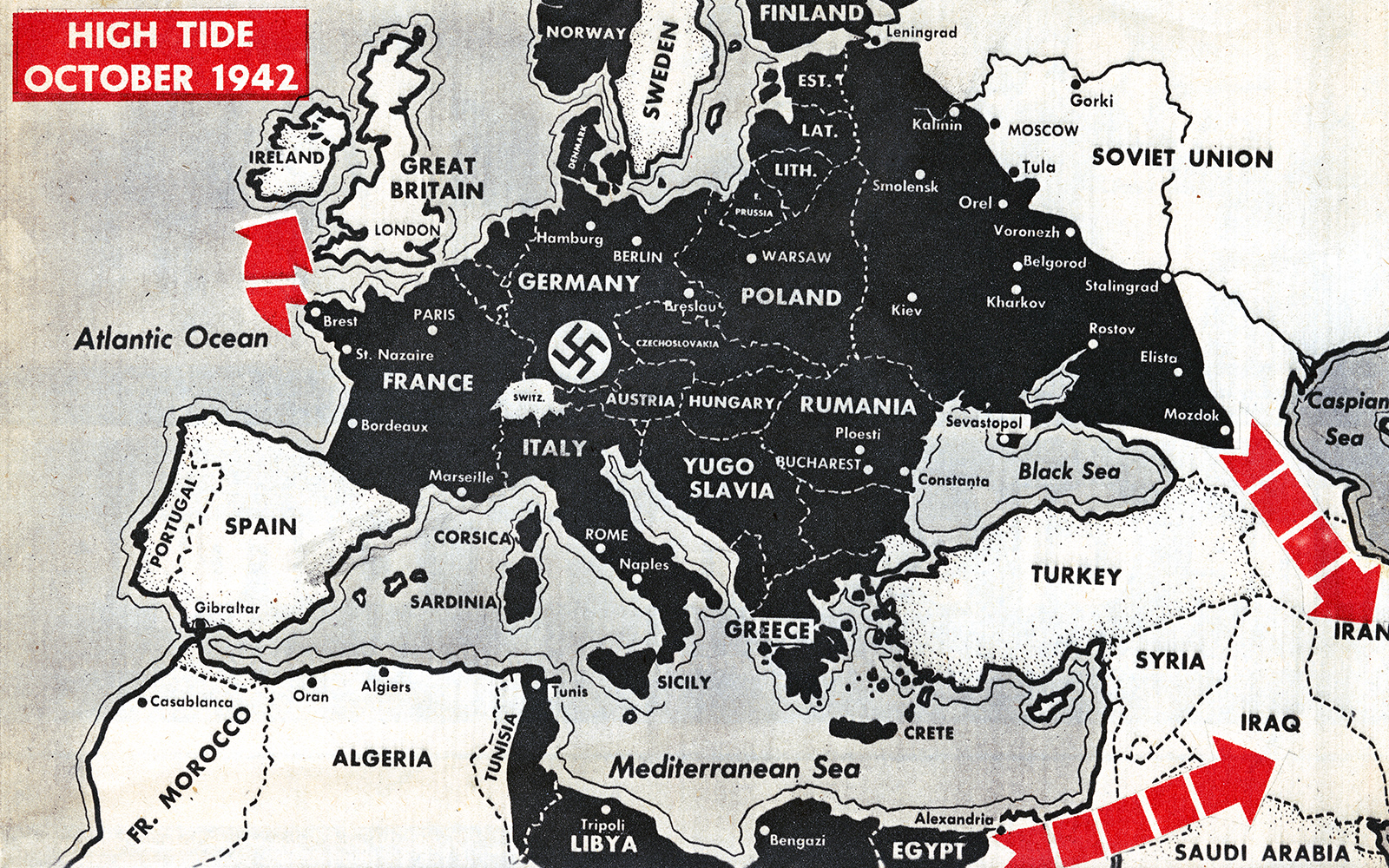 High Tide of Axis Powers, 1942
High Tide of Axis Powers, 1942
 Atomic bomb dropped on Japan, 1945
Atomic bomb dropped on Japan, 1945
Although World War 11 started in 1939, prior events such as the Treaty of
Versailles (1919) and Global Depression (1929-1939) affected both Germany
and Italy, creating civil unrest that led to new politcal leadership. This
includes the elections of Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini, fascist
leaders who allied with the Soviet Union (Nazi-Soviet Pact of 1939) and
Japanese Empire against the Western powers such as Great Britain, France,
and the United States.
Prelude
In the aftermath of World War 1, Germany was forced to pay reparations to
the Allies as part of the War Guilt Clause, stating that Germany took full
responsibility for the war and damages that occured as a result. However,
the Allies refused to help the German economy recover; this led to negative
public sentiment towards Western Europe and allowed politicians such as Hitler
and Mussolini to gain the support of the people. The incompentence of the League
of Nations strategy of appeasment led to Hitler amassing power, culminating in the
Munich Agreement which Hitler blatantly violated, invading all of Czechoslovakia.
Hitler's invasion of Poland in 1939 officially began World War 11.
Early War 1939-1942
Hitler steamrolled Poland with a new military strategy called "blitzkrieg"
(German for "lightning war"). After, Poland was split between Germany and
the Soviet Union under secret conditions of the Nazi-Soviet Pact. France fell
in June of 1940, and the puppet Vichy Regime took over. The air Battle of Britain
began in July of 1940 and was the first time Hitler's advance was stopped. Britain's
technological advantage with radar and spitfire planes allowed the British to defend
against the Nazi forces.
In June 1941, Hitler launched a surprise attack against the Soviet Union,
pushing them back to Moscow and Stalingrad. However, the Nazis were unable
to defeat the Soviets before winter and the offensive stalled out. Japan launched
a surprise attack on the US navy at Pearl Harbor, Hawai'i but failed to
fully destroy it. This led to the American entry to the war. Japan began to invade
surrounding Pacific countries to create a sphere of influence, leading the UK, China,
and other countries to declare war on Japan. By 1942, the Axis powers had reached
their "high tide" in Europe; from then on they would not advance their borders any further.
End of the War 1943-1945
By 1943, the German Army had been pushed mostly out of Russia. The disastrous
decision to attack Stalingrad rather than Moscow led to Hitler's defeat. The
Soviet Union would ally with Great Britain and the United States. In 1943 Italy
was the first Axis nation to surrender, isolating the Nazis in Europe. On June 6,
1944 the Allies landed in France, launching the invasion know as D-Day. France was
liberated by August and the Japanese had been pushed back from several islands in
the Pacific. Hitler commited suicide on April 30, 1945, signalling the end of Nazi
Germany. The United States dropped atomic bombs on Japan in August of 1945, leading
the Japanese to surrender. In the aftermath of the war, Germany was split between the
Western Allies and Soviet Union and Japan was rebuilt under US supervision.
 Treaty of Versailles, 1919
Treaty of Versailles, 1919
 Nazi-Soviet Pact, 1939
Nazi-Soviet Pact, 1939
 German tanks used in blitzkrieg, 1939-1942
German tanks used in blitzkrieg, 1939-1942
 High Tide of Axis Powers, 1942
High Tide of Axis Powers, 1942
 Atomic bomb dropped on Japan, 1945
Atomic bomb dropped on Japan, 1945